|
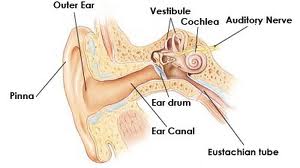
When a patient can't hear the doorbell ring,there may be damage in the inner ear
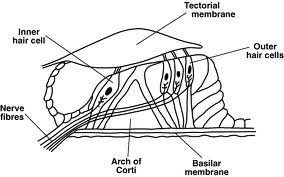
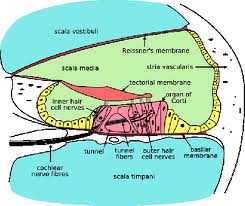
Cochlear & Retrocochlear DisordersInner ear disordersA sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage or a disorder of the inner ear, or of the auditory nerve, nerve fibres going from the inner ear to the brain stem. A hearing loss involving the inner ear or auditory nerve is impossible to treat medically. Amplification cannot satisfactorily compensate for some sensorineural hearing losses when damage or degeneration of the Organ of Corti, or auditory nerve fibres is extensive. The higher frequencies are usually affected in sensorineural loss. The person has difficulty in hearing high frequency consants like f,th,and s.This person cannot hear the difference between the words thin,fin, pin, shin, sin, skin. The person may also fail to hear a high pitched doorbell, a telephone ringing, or the signal lights in a car.Organic Hearing LossOrganic disorders involve physical damage to the hearing mechanism, neural pathways or the brain. Recruitment is a characteristic of many sensorineural cochlear losses. RecruitmentRecruitment occurs when a small increase in sound intensity results in a rapid increase in apparent loudness. A person with recruitment may barely be able to hear a sound of moderate intensity , but a sound of slightly greater intensity seems unbearably loud.
TinnitusTinnitus is often present in combination with sensorineural hearing losses and usually precedes it. IKt is described as a high frequency or buzzing noise. Tinnitus can be heard in one ear only, usually the ear with the greatest loss. It may be present in the other ear too, but is not noticed until the tinnitus is reduced on the loudest side. Amplification with a hearing instrument may reduce or eliminate the tinnitus. A hearing instrument is not a cure for tinnitus, the tinnitus returns when the hearing instrument is removed. Tinnitus can be treated holistically VertigoVertigo is a hallucination of movement, arising from problems within the vestibular portion of the inner ear. The world spins about the patient, or the patient feels that there is moving in space. Dizziness is a giddy or swimming sensation, and is not vertigo. Any disorder, tumor, infection or traumacausing a unilateral decrease in vestibular function may cause vertigo. Vertigo is common in Menieres syndrome and in central disorders such as epoilepsy, multiple sclerosis, strokes, tumors,i.e, acoustic neuroma and anemia. Acoustic TraumaAlso causes sensorineural loss. The inner ear is traumatized by exposure to a single very loud sound, explosion, or high noise levels for a long time. Noise Induced Hearing LossIs a sensorineural loss resulting from exposure to high noise levels. The exposure may be work related, or recreational. Industry is much more aware of the problems caused by noisy work environments. Regular hearing tests are carried out to establish the hearing thresholds of employees. Temporary Threshold ShiftAlso known as auditory fatigue, is a reversible drop in hearing thresholds from noise exposure.
PresbycusisIs a common type of sensorineural loss , it simply means hearing loss resulting from the ageing process. Toxins,Poisons, & DrugsOf many kinds affect hearing and cause a sensorineural loss. Toxins are produced by viral infections. Such diseases as whooping cough, measles, influenza, scarlet fever, mumps, diphtheria, meningitis, encephailitis, chicken pox, and viral pneumonia can wreak havoc with the inner ear. Poisons include carbon monoxide, lead, mercury, gold, arsenic, tobacco and alcohol. Each has an effect on the inner ear.Ototoxic drugs that cause sensorineural loss include, quinine, streptomycin, neomycin and kanamycin. Even common drugs, like aspirin, can cause a temporary threshold shift and tinnitus, although this is reversible when the use of aspirin is discontinued.
Congenital Sensorineural LossSensorineural loss means which was present at birth. There are two types, genetic or inherited and non-genitic or acquired. Sudden DeafnessIs caused by vascular occlusion, virus, or rupture of the round window membrane. Meniere’s SyndromeIs an excess of endolymphatic fluid .This sensorineural loss is a disorder of the entire inner ear, not just the cochlea.Symptons include the triad of vertigo, tinnitus and hearing loss. TumorsThe most common is an acoustic neuroma (V111 nerve tumor) which develops just outside the internal auditory meatus. It usually involves the vestibular and facial nerves as well. Symptoms include vertigo, tinnitus, facial paralysis, and unilateral hearing loss. A characteristic is the inability to understand speech. Removal of the tumor often leaves a dead ear. Oval Window FistulaIs a rupture of the stapes footplate, or of the annular ring, with a loss of perilymph fluid. It is caused by a trauma, or a sudden increase of intracochlear pressures. Round Window FistulaOccurs as a result of a direct trauma, barotraumas or increased perilymph pressures. LabyrinthitisIs an inflammation or infection of the inner ear. Temporal Bone TraumaA fracture of the temporal bone, results from automobile accidents or blows to the head. Some fractures are visible on the eardrum, itself. Central DeafnessOccurs through damage or disorders within the brain or brainstem. It is caused by 1. A tumor or ascess 2. Syphilis 3. Arteriosclerosis 4. Multiple sclerosis 5. Rh incompatibility 6.Cerebral v ascular Accidents, Brain hemorrhage,Strokes, Gunshot wounds 7.Lack of oxygen to the brain (a) drowning (b) Carbon monoxide poisoning
Non Organic Hearing LossIndividuals believe they have a hearing loss when there is nothing physically wrong with their hearing.
|